Hepatobiliary Pancreatic Surgery
Hepatologist in Pune
- Bile production, which is essential to digestion.
- Filtering of toxins from your body.
- Excretion of bilirubin, cholesterol, hormones, and drugs.
- Breakdown of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
- Activation of enzymes.
- Area of glycogen (a form of sugar), minerals, and vitamins (A, D, E, and K).
- Synthesis of blood proteins, such as albumin.
Types
Hepatitis has various types, but the signs & symptoms of each are related. Hepatitis can take acute or chronic forms. The three main types of hepatitis are known as hepatitis A, B, and C. Each is caused by a different virus.
Hepatitis A
It is usually easy for most patients make a full recovery, after which they are free and therefore protected from the virus in the future. However, if it progresses, symptoms can be severe. There is a vaccination available against this virus.
The virus most usually spreads when you eat or drink something contaminated with faecal matter. There is no specific treatment for HAV. The Hepatologist will advise the patient to abstain from alcohol and drugs during the recovery.
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is spread through contact with infected blood, semen, and some other body fluids. It can be a sexually transmitted disease (STD).
The liver of a person affected with hepatitis B swells. This can create severe injury and the infection may become chronic too. This can lead to complications, including scarring of the liver, or cirrhosis. It may also cause a type of cancer known as hepatocellular carcinoma. There is a safe and effective vaccine that can protect against Hepatitis B virus (HBV).
A patient with HBV requires full rest and avoid alcohol completely. The doctor may prescribe antiviral suppressive therapies.
Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) can lead to liver harm and swelling. Approximately 1 in 4 people with HCV get cirrhosis, and this can lead to liver cancer. A person contracts the HCV by coming into contact with infectious fluids and secretions from someone else who is already infected.
There is no vaccine to stop HCV, but medication can cure it. A mixture of therapies is now available to treat the hepatitis C virus based on its subtype. These methods target viral replication and stop the virus from being able to reproduce. When taken accurately, the cure percentage is very high.
Symptoms
Many people with hepatitis fill either mild or no indications. When symptoms develop, they can do so from 15 to 180 days after infection. This rule is common for all types of hepatitis.
Acute Hepatitis
The first phase of hepatitis is called the acute phase. The indications are similar to mild flu, and may include:
· Diarrhoea.
· Fatigue.
· Nausea and vomiting.
· Weight loss.
· Jaundice.
· Loss of appetite.
· Mild fever.
· Muscle or joint aches.
· Slight abdominal pain.
The acute phase is normal, however, it may progress to a chronic infection. This is most likely with HBV or HCV.
As the disease progresses, chronic hepatitis can lead to progressive liver failure, resulting in jaundice, swelling of the lower extremities, and blood in the faeces or vomit.
Prevention
Hepatitis can be serious and tough to treat, so people are encouraged to take precautions against any possible infection.
Preventing Hepatitis A
The following steps can help avoid infection:
- Wash hands with soap after using the bathroom.
- Only consume food that has just been cooked.
- Only drink boiled water.
- Get vaccinated.
Preventing Hepatitis B
To minimize the risk of transmission:
- Only use previously unused, clean needles.
- Do not share toothbrushes, razors, or manicure instruments.
- Ensure use of the use of well-sterilized instruments for a tattoo, piercing, or acupuncture.
- Get vaccinated.
How to Prevent Hepatitis C
To minimize the risk of transmission:
- Do not share needles, toothbrushes, or manicure equipment.
- Make sure equipment is well-sterilized for any skin piercing.
- Consume alcohol with moderation.
- Do not inject illegal drugs.
Do you notice any Hepatitis symptoms? Consult Dr. Sachin Palnitkar is best Hepatologist in Pune & Gastroenterologist in Pune at our Dr. Palnitkar gastro clinic for further tests and diagnosis.
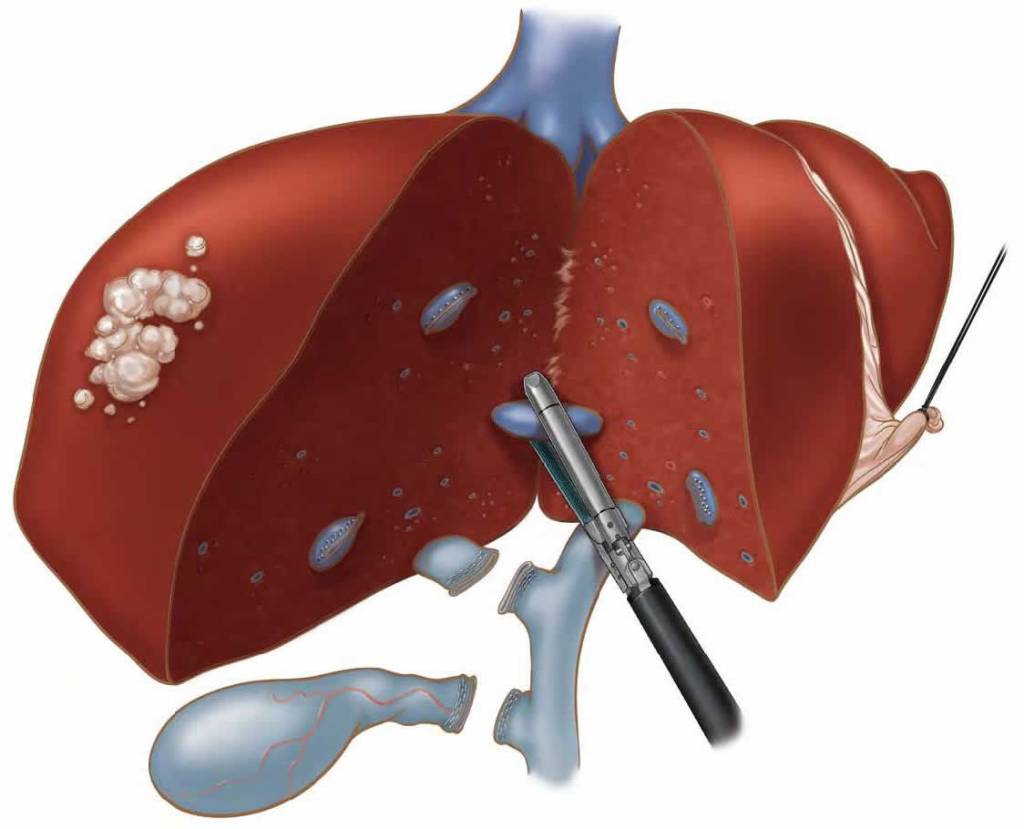
What is hepatobiliary and pancreatic surgery ?
The liver, pancreas, gall bladder and bile duct are known as the hepatobiliary and pancreatic system. Surgery to treat cancers and disorders in these organs is highly complicated and challenging and requires a high level of skill and expertise.
Hepatobiliary and pancreatic surgery can be performed using minimally invasive techniques. Some common procedures include:
* Removal of the distal (lower) stomach with the Whipple procedure
* Anti-reflux surgery for the gastrointestinal system
* Removal of part of the pancreas
* Removal of the gall bladder and reconstruction of the bile duct
* Liver transplant and liver resection (removal of all or part of the liver).
Why do you need hepatobiliary and pancreatic surgery
Hepatobiliary and pancreatic surgery are used to treat cancers and diseases of these organs. It includes the resection (removal) of primary and metastatic (secondary) tumors of the liver, gall bladder, bile duct, and pancreas. It is also used to treat benign diseases like cysts, bile duct injuries and strictures (blockage), and portal hypertension. Some tumors affecting the liver, gall bladder, and bile duct might need major resections, and might, therefore, need complex reconstruction of the bile duct, hepatic artery, and portal vein.
Such procedures involve a multidisciplinary team to provide an individualized treatment plan for each patient. This team of specialists and clinicians include hepatobiliary and transplant surgeons, medical oncologists, interventional radiologists, radiation oncologists, gastroenterologists, and ganesthesiologists.
Types of hepatobiliary and pancreatic surgery
1. Whipple
2. Cholecystectomy
3. Hepatectomy
Whipples
The Whipple Procedure or pancreaticoduodenectomy is the most commonly performed surgery to remove tumors in the pancreas. In a standard Whipple procedure, the surgeon removes the head of the pancreas, the gallbladder, part of the duodenum which is the uppermost portion of the small intestine, a small portion of the stomach called the pylorus, and the lymph nodes near the head of the pancreas. The surgeon then reconnects the remaining pancreas and digestive organs so those pancreatic digestive enzymes, bile, and stomach contents will flow into the small intestine during digestion. In another type of Whipple procedure known as pylorus-preserving Whipple, the bottom portion of the stomach, or pylorus, is not removed. In both cases, the surgery usually lasts between 5-8 hours.
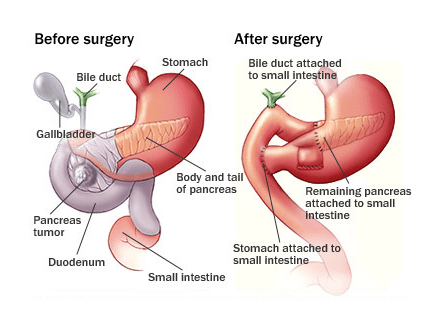
After a Whipple procedure, the most common complication is delayed gastric emptying, a condition in which the stomach takes too long to empty its contents. Usually, after 7-10 days the stomach begins to work properly. If delayed gastric emptying persists, supplemental feedings by a feeding tube may be started. The condition usually lasts for another 7-10 days but could last as long as a few weeks. The most serious potential complication is abdominal infection due to leakage where the pancreas has been connected to the intestine. This occurs in approximately 10% of patients and is usually managed by a combination of draining tubes, antibiotics, and supplemental tube feedings. Patients who have undergone the Whipple procedure may experience long-term effects including digestive difficulties.
Leading Hepatologist in Pune Dr. Sachin Palnitkar is expert in Liver diseases and experienced gastroenterologist in Pune.
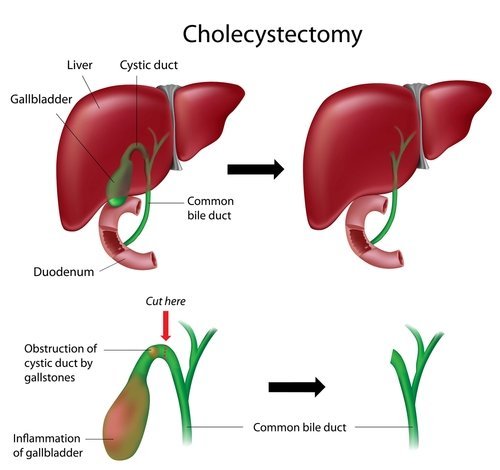
Cholecystectomy
Cholecystectomy is a surgical procedure to remove your gallbladder – a pear-shaped organ that sits just below your liver on the upper right side of your abdomen. Your gallbladder collects and stores bile – a digestive fluid produced in your liver.
Cholecystectomy may be necessary if you experience pain from gallstones that block the flow of bile. Cholecystectomy is a common surgery, and it carries only a small risk of complications. In most cases, you can go home the same day of your cholecystectomy.
Cholecystectomy is most commonly performed by inserting a tiny video camera and special surgical tools through four small incisions to see inside your abdomen and remove the gallbladder. Doctors call this laparoscopic cholecystectomy. In some cases, one large incision may be used to remove the gallbladder. This is called an open cholecystectomy.
Hepatectomy
Hepatectomy is the surgical resection or the complete removal of the liver. While this procedure can also be performed to “harvest” healthy liver tissue, it is mostly performed to remove diseased parts of the organ to treat certain conditions such as benign hepatic neoplasms and cancer.
Liver resection is often recommended for patients suffering from malignant or benign hepatic neoplasms, including the following:
* Hepatocellular adenoma
* Hepatic hemangioma
* Focular nodular hyperplasia
* Metastases to the liver
* Hepatocellular carcinoma